반응형
SMALL
문제
Given the root of a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from top to bottom, column by column).
If two nodes are in the same row and column, the order should be from left to right.
Example 1:
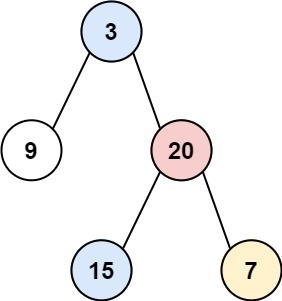
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Example 2:
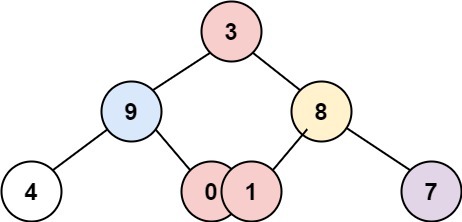
Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7]
Output: [[4],[9],[3,0,1],[8],[7]]
Example 3:
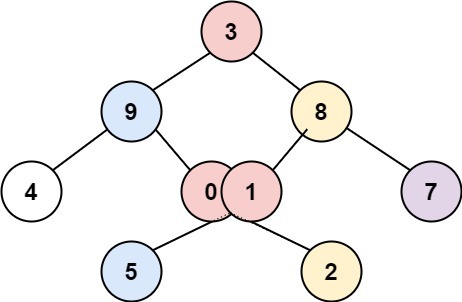
Input: root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7,null,null,null,2,5]
Output: [[4],[9,5],[3,0,1],[8,2],[7]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
문제풀이
가장 root를 level 0이라고 두고
왼쪽은 level - 1, 오른쪽은 level + 1이라고한다
level을 key로, 노드 값은 배열안의 value로 해서
level 별로 정리 후 배열로 재생산
코드
// BFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var verticalOrder = function(root) {
const obj = {};
let queue = [[root, 0]];
while(queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
const n = node[0];
const level = node[1];
if(!n) return [];
if(obj[level]) {
obj[level].push(n.val)
} else {
obj[level] = [n.val];
}
if(n.left !== null) queue.push([n.left, level - 1]);
if(n.right !== null) queue.push([n.right, level + 1]);
}
const ret = [];
Object.keys(obj).sort((a,b)=>a-b).forEach((a) => ret.push(obj[a]));
return ret;
}
반응형
LIST
'Coding Interview' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] BFS-DFS 207. Course Schedule (feat. 위상정렬(Topological Sort)) (1) | 2022.09.25 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] DFS-BFS 329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix (1) | 2022.09.25 |
| [LeetCode] BFS-DFS 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (2) | 2022.09.24 |
| [LeetCode] BFS-DFS 200. Number of Islands (0) | 2022.09.24 |
| [기초] BFS와 DFS (0) | 2022.09.22 |